Augmented Reality Animation | Trinity Animation
One of the marketing trends attracting a lot of attention these days is augmented reality or “AR.” As the required hardware has become less expensive and more commonly available, this technology has become better known and more popular.
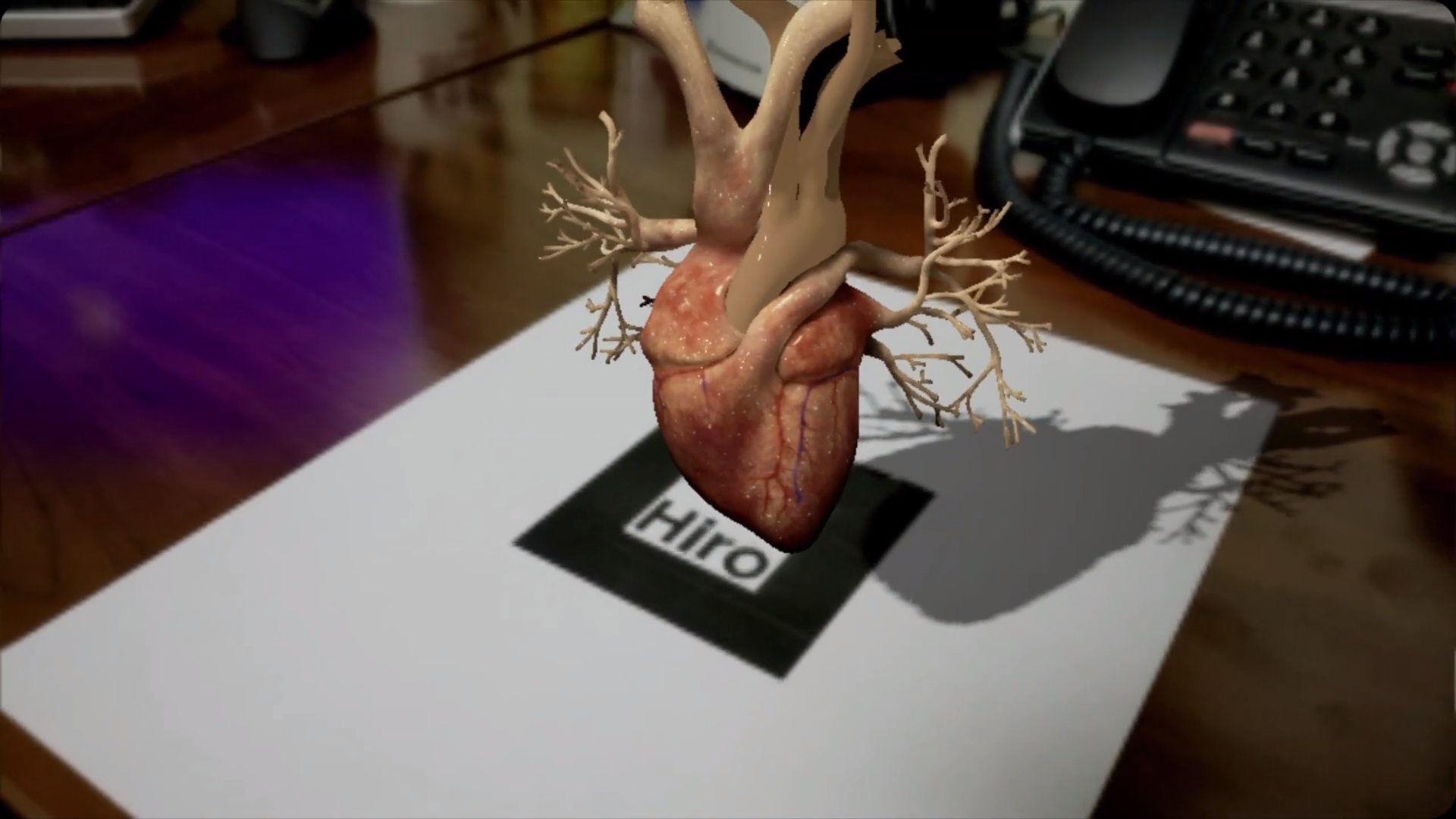
An augmented reality animation example that can help explain how AR works is shown below (AR Heart Tech Demo by Trinity Animation). Boiled down to its essentials, augmented reality animation software creates an image or 3D object that the software then blends into a real-life background. The combined image is viewed through the camera aperture of a cell phone. So, as the name implies augmented reality animation adds something to the reality that wouldn’t otherwise be there. The blending can be convincing that it is hard to see what is a solid object in the environment and what is an AR overlay image or object.
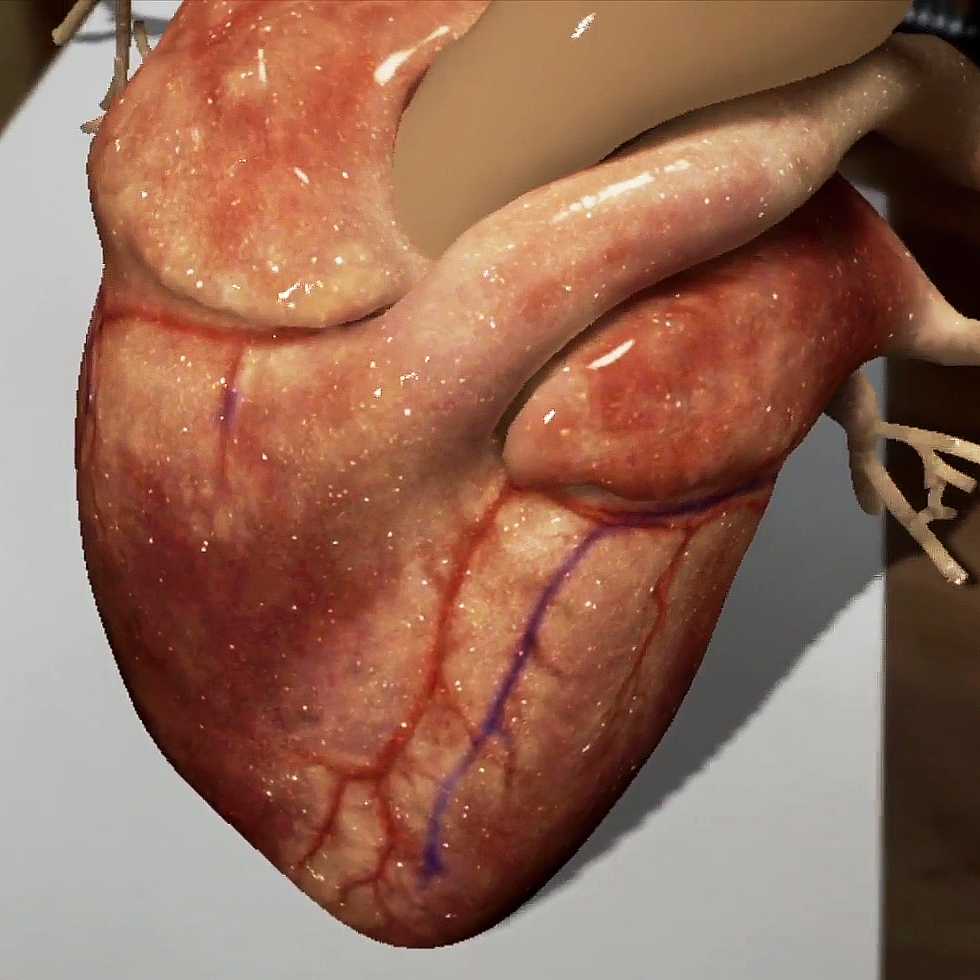
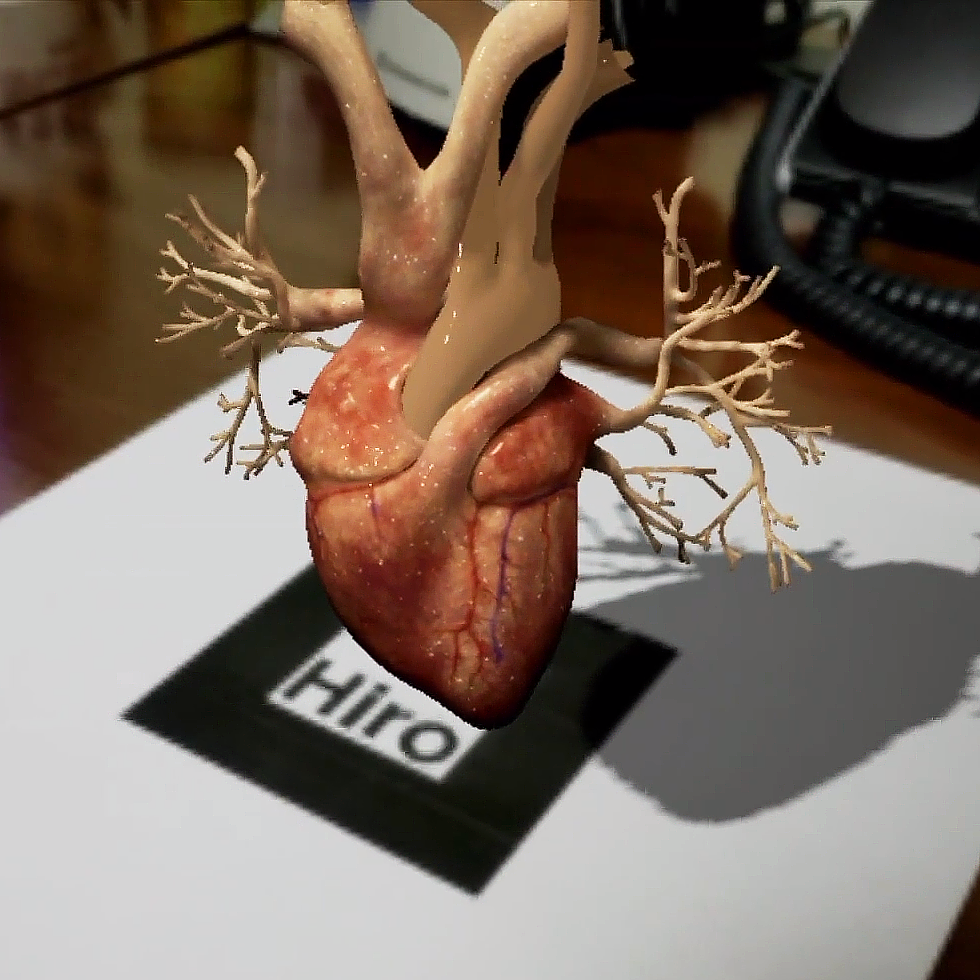
Take a look at this beating heart AR example created by our artists here at Trinity.
The first step in the AR Heart Tech Demo) was the modeling of a realistic human heart in 3 dimensions. The heart is animated to show the rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle. Special augmented reality animation software is loaded on a cell phone and the viewer looks through the cell phone camera aperture. The viewer sees a beating heart suspended above the flat surface. The beating heart can be enlarged, turned at any angle, and examined in detail by the viewer. Virtual reality like this could be useful in biology classes and used to help healthcare students learn human anatomy.
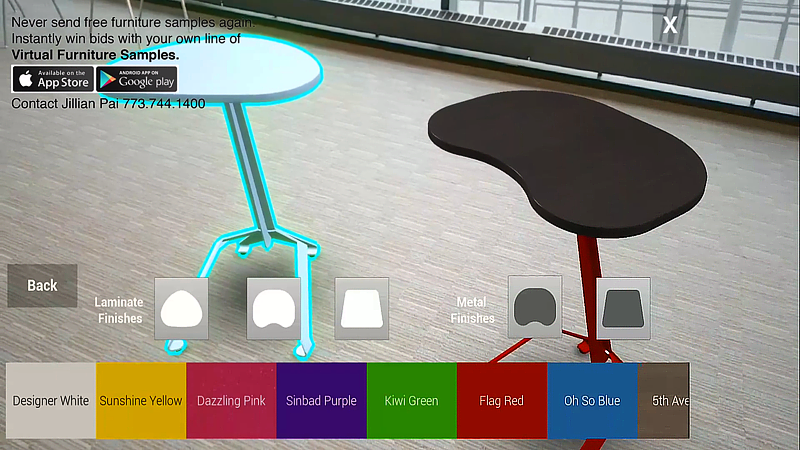
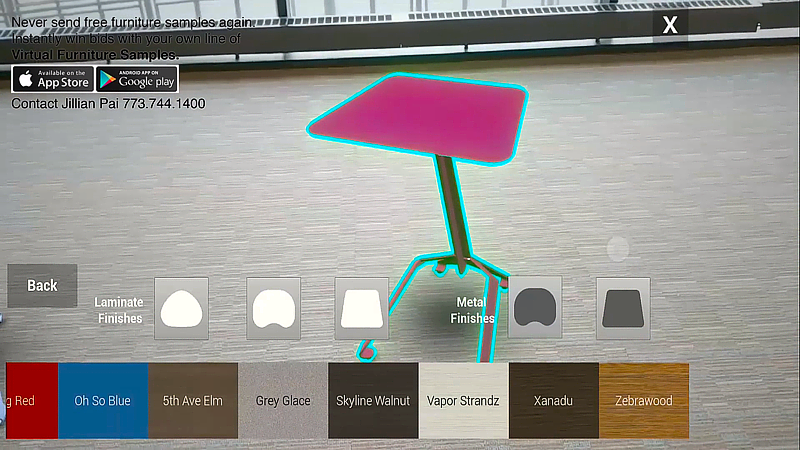
Another example of AR demonstrates how AR can be a very practical tool in daily life.
In this example, we have modeled certain office tables and created choices as to style, size, and form. The AR software is loaded onto the cell phone and be carried anywhere the cell phone can be carried.
A potential furniture buyer can use the AR software to very accurately show what a particular piece of furniture would look like in their own office or home. The furniture customer can change colors and styles until he or she finds a piece that looks great in the particular part of the room which additional furniture is needed.
Currently, there are at least four types of augmented reality:
- [a] markerless augmented reality. This technology uses the GPS or digital compass software which commonly runs on a commercial cell phone. It is commonly used for navigation. The user can call up images which provide real-time directions and assistance in finding nearby businesses of points of interest.
- [b] marker-based augmented reality. This method uses a camera (commonly a cell phone camera) and some type of visual marker such as a QR code to generate an image when the marker is sensed by the reader. One advantage of this approach is that simple patterns are used as markers, as they can be easily recognized.
- [c] projection-based augmented reality. This technology projects artificial light into real-world surfaces.
- [d] superimposition-based augmented reality. This approach to VR replaces the view of the object with an augmented of the same object. IKEA has developed this technology into a usable form for its customers.
What are QR codes?
A quick response code (QR Code) is just a variation on the familiar barcode. It was developed by Denso Wave Corporation in 1994, originally for use as vehicle trackers in the auto industry. The QR code square can hold a broad range of information which can be accessed by scanning the code with an ordinary personal cell phone, just as grocery product barcodes are scanned at grocery stores. QR codes can take static or dynamic forms. As might guess from the term
“static” these QR codes contain a fixed amount of information including items such as: a web address(URL), wifi access details, e-mail address, phone number, calendar event and the like. A “dynamic” QR contains a code that directs the viewer to a target web address. The advantage of to the author of the dynamic QR code is that the target website can be edited and updated at any time. The owner author of the QR can also track scanning activity and therefore learn details about who is scanning the QR, where it is being scanned and how often.